The Certified Ethical Hacker (C|EH) credentialing and provided by EC-Council is a respected and trusted ethical hacking course in the industry. Since the inception of Certified Ethical Hacker in 2003, the credential has become one of the best options for industries and companies across the world. The C|EH exam is ANSI 17024 compliant, adding value and credibility to credential members. It is also listed as a baseline certification in the US Department of Defense (DoD) Directive 8570 and is a NSCS Certified Training.
Today, you can find Certified Ethical Hackers working with some of the finest and largest companies across industries like healthcare, financial, government, energy and much more!
An Ethical Hacker Answers the Following Questions:
- What kind of vulnerabilities does an attacker see?
- What information or system would a hacker most want access?
- What can an attacker do with the information?
- How many people notice the attempted hack?
- What is the best way to fix the vulnerability?
Ethical hackers learn and perform hacking in a professional manner, based on the direction of the client, and later, present a maturity scorecard highlighting their overall risk and vulnerabilities and suggestions to improve.
Importance of Ethical Hacking?
In the dawn of international conflicts, terrorist organizations funding cybercriminals to breach security systems, either to compromise national security features or to extort huge amounts by injecting malware and denying access. Resulting in the steady rise of cybercrime. Organizations face the challenge of updating hack-preventing tactics, installing several technologies to protect the system before falling victim to the hacker.
New worms, malware, viruses, and ransomware are primary benefit are multiplying every day and is creating a need for ethical hacking services to safeguard the networks of businesses, government agencies or defense.


Government agencies and business organizations today are in constant need of ethical hackers to combat the growing threat to IT security. A lot of government agencies, professionals and corporations now understand that if you want to protect a system, you cannot do it by just locking your doors
Jay Bavisi
CEO of EC-Council
Benefits of Ethical Hacking?
- Discovering vulnerabilities from an attacker’s POV so that weak points can be fixed.
- Implementing a secure network that prevents security breaches.
- Defending national security by protecting data from terrorists.
- Gaining the trust of customers and investors by ensuring the security of their products and data.
- Helping protect networks with real-world assessments.
Practice ethical hacking to Ensure Safe Stay at Home

Types of Ethical Hacking?
Web Application Hacking

System Hacking
Web Server Hacking
Hacking Wireless Network

Social Engineering
Types of Hacking/Hackers
Hackers are of different types and are named based on their intent of the hacking system. Broadly, there are two main types in hacking/hacker – White-Hat hacker and Black-Hat hacker. The names are derived from old Spaghetti Westerns, where the good guy wears a white hat and the bad guy wears a black hat.

White Hat Hacker
Ethical hackers or white hat hackers do not intend to harm the system or organization but they do so, officially, to penetrate and locate the vulnerabilities, providing solutions to fix them and ensure safety.

Black Hat Hacker

Gray Hat Hacker
Core Concepts of System Hacking
Phases of Ethical Hacking
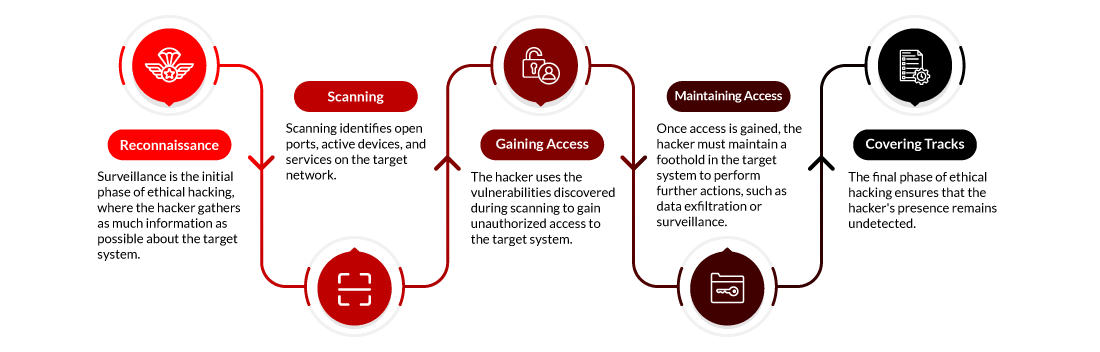
The five phases of ethical hacking are:
1. Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance is the first step in ethical hacking. It’s often referred to as footprinting. Here, a hacker tries collecting various kinds of data, such as employee information, IP addresses, network topology, and domain names, using active and passive approaches. The purpose is to create a diagram of the target’s digital and physical assets.
Active Reconnaissance: This method involves direct interaction with the target system, which may warn the target about possible scans.
Passive Reconnaissance: This implies collecting data without direct contact with the target, making it untraceable.
Popular Tools Used are:
- Nmap
- Whois
- Maltego
Reconnaissance Techniques Commonly Used:
- Google Dorking: Utilizing sophisticated search operators to find sensitive information online.
- Whois Lookup: Collecting information on who owns the domain, IP addresses, etc.
- Social Engineering: Mupulating people into revealing private information regarding targets; this can be done through phishing messages, for instance.
- DNS Enumeration: To create a topology of the target’s infrastructure by finding all DNS entries linked with the domain name concerned.
- Network Scanning: One can learn about active systems and running services using tools like Nmap.
2. Scanning
- Port Scanning: Finding open ports or services with Nmap or Angry IP Scanner.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Detecting known weaknesses in systems and applications using Nessus.
- Network Mapping: Creating a blueprint of network topology with tools such as SolarWinds.
Popular Tools Used:
- Nessus
- OpenVAS
- Angry IP Scanner
Commonly used techniques for Scanning
- Port Scanning: Using tools like Nmap or Angry IP Scanner to find open ports or services.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Using tools like Nessus to detect known weaknesses in systems and applications.
- Network Mapping: Generating a visual map that shows the network topology with applications like SolarWinds.
- Banner Grabbing: This involves collecting software version information from open services to help determine any weaknesses.
- Ping Sweeps: This entails sending ICMP requests to identify active hosts on a particular network.
3. Gaining Access
Popular Tools Used:
- Metasploit
- SQLmap
- Hydra
Commonly used techniques for Gaining Access:
- Password Cracking: Using brute force and dictionary attacks or to crack passwords, rainbow tables are used.
- Exploration of Vulnerabilities: Unauthorized access can be obtained by exploiting known vulnerabilities such as SQL Injection or buffer overflows.
- Privilege Escalation: Higher-level privileges are acquired within a system through exploitation or misconfiguration.
- Session Hijacking: Taking over a valid session between a user and a system gives entrance without permission.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks: By intercepting communication between two parties, sensitive data can be accessed, violating confidentiality principles.
4. Maintaining Access
Tools Used:
- Netcat
- Ngrok
- Empire
Standard Methods of Maintaining Access:
- Installing Backdoors: Creating permanent ways of accessing the system later, like backdoors or rootkits.
- Creating Hidden User Accounts: Adding unauthorized users with administrative privileges that are hard to discover.
- Tunneling: Employing strategies such as SSH tunneling for secure communication with an infected machine.
- Keystroke Logging: Capturing user’s keystroke entries to acquire confidential details such as passwords or private information.
- Trojan Horses: Integrating applications that look real but permit unlawful entry.
5. Clearing Track
Tools Used:
- CCleaner
- Stealth Rootkit
- Timestomp
Standard Methods For Covering Tracks:
- Log Tampering: Deleting or modifying logs to erase evidence of hacking activities.
- Steganography: Hiding malicious files or data within legitimate files to avoid detection.
- File Timestamp Alteration: Changing the timestamps of modified files to mislead investigators.
- Clearing Command Histories: Deleting or altering shell command histories to prevent detection.
- Encryption: Encrypting communication and files to obscure activities makes forensic analysis more difficult.
These are the five steps of the CEH hacking methodology that ethical hackers or penetration testers can use to detect and identify vulnerabilities, find potential open doors for cyberattacks and mitigate security breaches to secure the organizations. To learn more about analyzing and improving security policies, network infrastructure, you can opt for an ethical hacking certification. The Certified Ethical Hacking (CEH v12) provided by EC-Council trains an individual to understand and use hacking tools and technologies to hack into an organization legally.
At its core, the VAPT includes three certifications

CND: Certified Network Defender
The Certified Network Defender (CND) certification program focuses on creating network administrators who are trained in protecting, detecting, and responding to threats on a network. The course contains hands-on labs based on major network security tools and techniques which will provide network administrators real-world expertise on current network security technologies and operations. For more details on the CND program, visit the course page.

CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker
In its 12th version, the Certified Ethical Hacker provides comprehensive training, hands-on learning labs, practice cyber ranges for engagement, certification assessments, cyber competitions, and opportunities for continuous learning into one comprehensive program curated through our new learning framework: 1. Learn 2. Certify 3. Engage 4. Compete. For more details on the C|EH program visit the course page.

CEH (Practical): Certified Ethical Hacker
C|EH Practical is a six-hour exam that requires you to demonstrate the application of ethical hacking techniques such as threat vector identification, network scanning, OS detection, vulnerability analysis, system hacking, web app hacking, etc. to solve a security audit challenge. This is the next step after you have attained the Certified Ethical Hacker certification. For further information on C|EH (Practical), visit the course page.

Certified Ethical Hacker (Master)
C|EH (Master) is the world’s first performance-based ethical hacking industry readiness certification, that is verified, online, live, and proctored.
C|EH Master is the next evolution for the world-renowned Certified Ethical Hacker credential and a logical ‘next step’ for those holding the prestigious certification. Earning the C|EH Master designation is your way of saying, “I learned it, I understood it, and I proved it.”
EC-Council will award the C|EH (Master) certification to you if you clear the C|EH certification and the C|EH (Practical) credential.
Become a C|EH (Master) by clearing the C|EH (Practical) exam here
At the advanced level, the VAPT certification track includes three certifications

C|TIA: Certified Threat Intelligence Analyst
The Certified Threat Intelligence Analyst (CTIA) program was developed in collaboration with cybersecurity and threat intelligence experts across the globe to help organizations identify and mitigate business risks by converting unknown internal and external threats into known threats. It is a comprehensive, specialist-level program that teaches a structured approach for building effective threat intelligence. Visit the course page to learn more about the C|TIA program.
CPENT: Certified Penetration Testing Professional
The C|PENT program is a comprehensive course that encompasses an innovative and multi-disciplinary curriculum to help Cyber Professionals polish their skills and gain proficiency in performing effective penetration tests in real-world enterprise network environments.
The program covers advanced windows attacks, how to pen test IoT and OT systems, bypassing filtered networks, how to write your own exploits, single and double pivoting to gain access to hidden networks, how to conduct advanced privilege escalation as well as binary exploitation.
Through performance-based cyber challenges on live Cyber Range, C|PENT Cyber Range provides a hands-on and comprehensive practice based on real-world scenarios to help you gain an edge on penetration tests. The program’s curriculum is designed to help you become a world-class Certified Penetration Tester. If you desire to pursue this program, and ready to take the most difficult cyber challenge, you can visit our Course page to learn more about the CPENT program.

LPT (Master): Licensed Penetration Tester (Master)
The LPT (Master) program is designed to help you join the ranks of elite pen testers through an extensive curriculum based on rigorous real-world penetration testing challenges crafted by industry experts. The program aims to test your penetration testing skills against a multi-layered network architecture with defense-in-depth controls over three intense levels, each with three challenges. The challenges are time-bound; you will need to make informed decisions while choosing your approach and exploits under intense pressure at critical stages.
Suppose you score 90% on the CPENT live range exam. In that case, you will not only earn the C|PENT certification, but you will also obtain the prestigious Licensed Penetration Tester (LPT) Master Credential.
Find out what it takes to become the best in penetration testing on LPT (Master) course details page.











