An organization’s incident response plan is the set of measures and procedures it has in place to respond to and protect against a cyberattack. An effective incident response plan can reduce the damage experienced after a security breach and ensure faster systems recovery.
As the rates of cybercrime continue to increase, incident response plans have become indispensable to the organization’s security protocol. However, it’s important to understand why and how incident response strategies for cloud-based infrastructures and systems differ from traditional incident management.
Pillars of Information Security Management


The Steps of the Cloud Incident Handling Process
Incident Detection in the Cloud
An integral aspect of a company’s security infrastructure is incident detection, the practice of monitoring networks, servers, and IT assets for suspicious activity. Effective incident detection can find intruders in an organization’s infrastructure and chart appropriate incident response strategies.
Detecting security breaches in the cloud is a daunting task. Because traditional incident detection mechanisms are not effective in the cloud environment, it is important that organizations hire security experts who know how to effectively respond to cloud-based data breaches.
The Importance of Incident Response in the Cloud
In a perfect world, successful cyberattacks would never occur, but realistically, security breaches are unavoidable. Companies need secure plans and strategies to minimize the risks associated with security incidents.
If a security incident is identified, an incident response plan enables security teams to defend affected applications and infrastructures against compromises, insider threats, and access misuse. An effective incident response strategy can prevent excessive damage and reduce business disruption and enables organizations to quickly contain issues and respond effectively.
Reputation, revenue, and customer trust are at stake in the event of a cyberattack. The goal of any incident response plan is to restore operations as quickly as possible, minimize losses, and fix vulnerabilities.
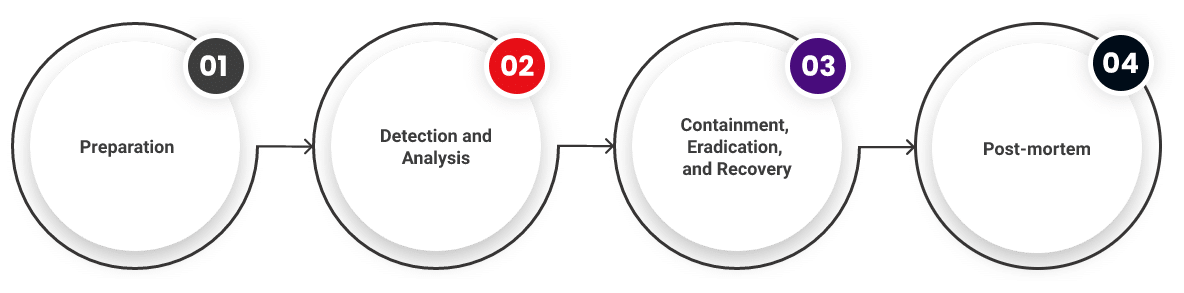
The Cloud Incident Response Life Cycle
Let’s look at the four phases of the incident response life cycle in the cloud.
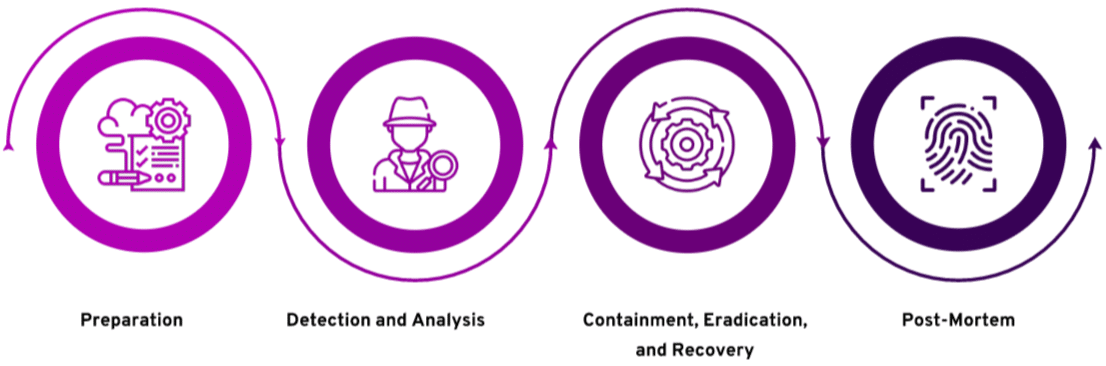
Preparation
Without predetermined guidelines, response teams cannot effectively address a security breach. Organizations must establish policies, procedures, and agreements for incident response management.
It’s important to create standards to enable seamless operations after an incident. Organizations must also conduct cyber awareness training for their employees as well as assessments to evaluate the efficacy of their incident response measures.
Detection and Analysis
Best Practices for Cloud Incident Response
Since millions are at stake, businesses constantly evolve their incident response practices to thwart cyberattacks. To maintain a strong cybersecurity posture, organizations must constantly iterate their incident management process.
Here are some best practices to secure cloud computing:
What is SOAR?

Let’s take a closer look at each of the elements of a SOAR platform:
- Security Orchestration: Facilitates seamless operation among multiple software and hardware components
- Automation: Executes security-related tasks, such as vulnerability scans and log searches, without human intervention and uses customized automations to handle organization-specific security risks
- Response: Uses pre-programmed strategies to respond to security threats—for example, by automatically isolating devices or interrupting transfers
Automation is a vital component of responding to security incidents in a cloud environment. Automating incident response helps organizations scale their capabilities, rapidly reduce the scope of compromised resources, and eliminate repetitive work by security teams. For instance, SOAR technology can be used as part of Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud incident response to unify workflows across cloud and on-premises infrastructures.
In today’s environment of widespread and sophisticated cyberthreats, SOAR platforms are key to managing the seemingly endless stream of cyberattack attempts that many organizations face. The main drivers for the rise in the adoption of SOAR technologies are the shortage of skilled cloud security professionals, the evolution of advanced cyberthreats, and increases in the number of security alerts.
Benefits of SOAR
For analysts overwhelmed by the growing volume of threat alerts received each day, SOAR platforms are an invaluable resource. The main purpose of a SOAR solution is to provide a standardized process for data aggregation that automates threat detection and response processes, reducing analysts’ workload and allowing them to focus on other mission-critical tasks.
For analysts overwhelmed by the growing volume of threat alerts received each day, SOAR platforms are an invaluable resource. The main purpose of a SOAR solution is to provide a standardized process for data aggregation that automates threat detection and response processes, reducing analysts’ workload and allowing them to focus on other mission-critical tasks.
Monitoring many security technologies can create enormous strain on security analysts. Instead of spending time on mundane tasks such as gathering and sorting through metrics and reports, cybersecurity personnel can relegate much of this work to the automation capabilities of SOAR platforms.
Automated incident response takes the heat-of-the-moment guesswork out of event handling, limiting cyberattack dwell time and overall business impact. SOAR platforms can help organizations improve their productivity and capacity to address more threats by allowing security staff to work smarter, not harder.
How Is SOAR Different from SIEM?
Security information and event management (SIEM) tools are software solutions that collect, analyze, and store security-related log data from various tools (e.g., firewall, IDS, IPS, antivirus software) and networking appliances (e.g., proxies) for compliance or auditing purposes. In simpler terms, SIEM platforms help organizations recognize potential threats and vulnerabilities before they can disrupt business operations, thereby enhancing data security in the cloud.
Though SOAR and SIEM platforms have a lot in common, there are differences in their capabilities. While both solutions collect data, they differ in the quantity and type of data they collect as well as the type of response they facilitate. Let’s take a closer look at some of the differences between SOAR and SIEM solutions:
SIEM tools only raise an alert when a potential threat is discovered. Security analysts need to intervene to investigate more closely, analyze the threat, and remediate any damage. This requires constant fine-tuning and development and often ends up being time-consuming. On the other hand, SOAR platforms reduce human intervention, as they automate the response process and filter out false positives, allowing security teams to handle the alert load quickly and efficiently.
Security Incident Response in AWS Cloud
Organizations using AWS Cloud should be prepared to detect and respond to security incidents and outline remediation methods that leverage automation to improve response speed.
AWS Cloud uses a shared responsibility model, meaning that AWS is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure while customers are expected to protect their data and networks. Security experts must continuously monitor the AWS Cloud environment and be ready to respond to and mitigate the impact of potential breaches.
The following steps provide the framework for AWS incident management:

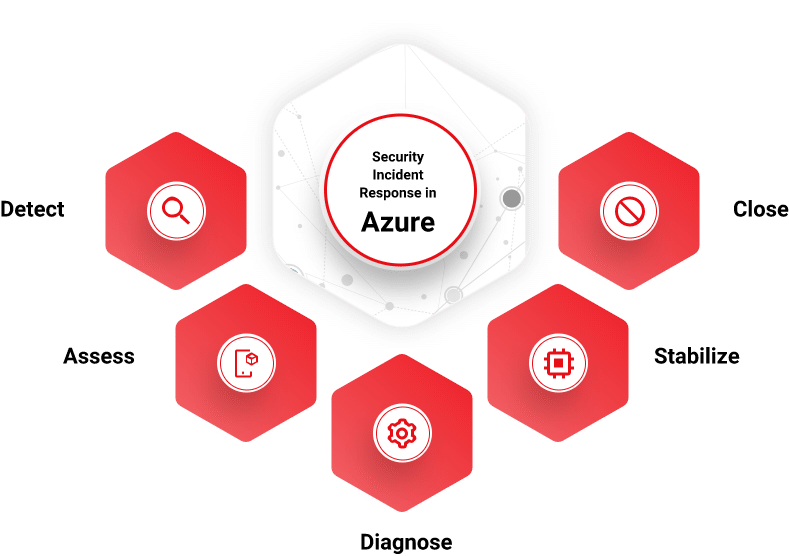
Security Incident Response in Microsoft Azure
Azure’s incident response life cycle is a five-step process:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-security-incident-response-guide/welcome.html
https://www.networkworld.com/article/3116011/best-practices-for-incident-response-in-the-age-of-cloud.html
https://hackernoon.com/7-effective-tips-to-secure-your-data-in-the-cloud-820bfe438d2
https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/artifacts/csa-cxo-trust-working-group-charter/
https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/blog/2021/11/13/how-the-incident-response-lifecycle-changes-for-cloud/
https://cloud.google.com/docs/security/incident-response
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/cloud-computing-industry
https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/artifacts/cloud-incident-response-framework/
https://www.lucidchart.com/blog/cloud-incident-response-best-practices
https://www.uptycs.com/blog/intrusion-detection-in-cloud-computing











